Contact Admission
International Collaboration
UPDATE KNOWLEDGE ON HOW VACCINE COVID-19 WORKS
UPDATE KNOWLEDGE ON HOW VACCINE COVID-19 WORKS
Bác sỹ Nguyễn Hữu Tùng
Updated March 9, 2021
Immune system - The body's defense system against infectious diseases
To understand how the COVID-19 vaccine works, first learn about how our bodies fight disease. When pathogens, like the virus that cause COVID-19, attack our bodies, they attack and multiply. This attack, also known as an infection, is the agent that causes disease. Our immune system is scattered throughout the body, in many organs and in many different forms. Blood contains red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the body's tissues and organs, and white blood cells or immune cells to fight infection. Different types of white blood cells fight infection in different ways:
Macrophages are lymphocytes that absorb and digest pathogens and cells that are dead or dying. The macrophages leave parts of the pathogen to invade, known as "antigens". The body identifies antigens that are considered dangerous and stimulates antibodies to attack them.
B lymphocytes are the white blood cells that protect the body. They create antibodies to attack virus fragments, bacteria ... macrophages left behind.
T lymphocytes are the type of white blood cells that protect the body. They attack cells in the body that are already infected.
The first time a person is infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, it can take days or weeks for their bodies to make and use all of their body's immune systems to find ways to fight off the pathogen. infection. After an infection, the body's immune system remembers traces of the virus and continues to provide future protection against the disease.
The body stores a few T-lymphocytes, called "memory cells," that rapidly act if the body encounters the same virus again. When similar antigen is detected, B lymphocytes produce antibody against them. Experts are still investigating how long these memory cells protect a person from the COVID-19 virus, known as the antibody titer / which is the concentration of circulating antibodies in the blood after injection. prevention or post-viral infection (infection).
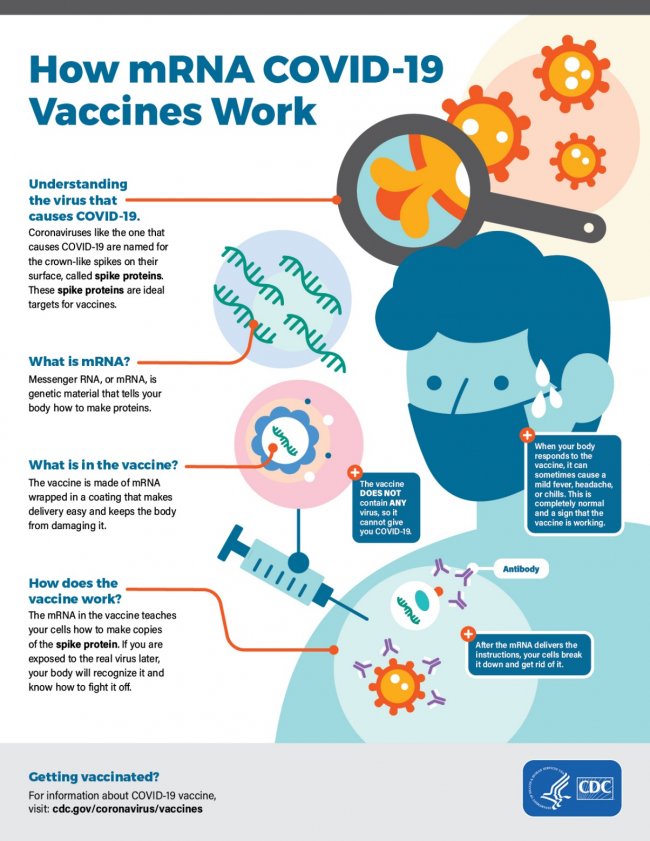
How COVID-19 vaccine works
The COVID -19 vaccine helps our bodies develop immunity against the virus that causes COVID-19, in this case is called active immunization, which is different from passive immunity, in which the body produces anti-super antibodies. en after being infected with the virus. Different vaccines act in different ways to provide protection. But with all vaccines, when introduced into the body it triggers the immune system to produce a "memorizing" T-cell line as well as B-lymphocytes that produce antibodies against the virus in the body. future.
Usually, a few weeks after vaccination, the body produces T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes. Therefore, there may be cases where a person becomes infected with the COVID-19 virus just before or immediately after the vaccination. , then the Covid-19 test can still be positive, in this case the medicine called window period viral exposure.
Vaccines
There are currently three COVID-19 vaccines that have been approved and recommended for use, or are undergoing extensive clinical trials (Phase 3) in the United States. Below is a description of the structure of each covid-19 vaccine. None of these vaccines cause COVID-19 in humans.
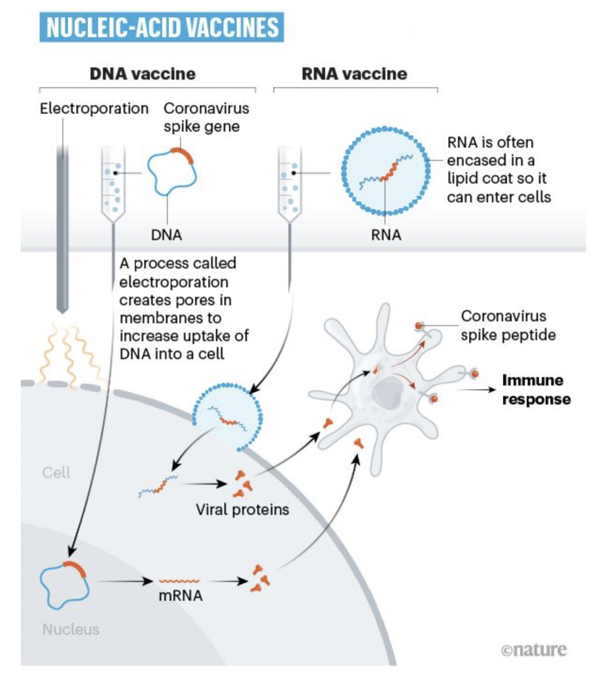
Vaccine mRNA vaccine messenger RNA), Vaccine Pfizer / BioNtech, Moderna are mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccine is also called the messenger vaccine. When the vaccine is injected into the body, the vaccine contains an object from the SAR-COV2 virus that will travel to the cell and the cell will produce a harmless foreign protien or "mutant protein" that carries the virus's seal. there. After our cells make those protein copies, they destroy the genetic material from the Covid-19 vaccine and leave only this mutant protein powder. Our body will detect this foreign protein and present it to T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes will remember this antigen marker and produce antibodies against the Covid-19 virus if we are infected. disease in the future.
Mechanism of action of vaccine mRNA:
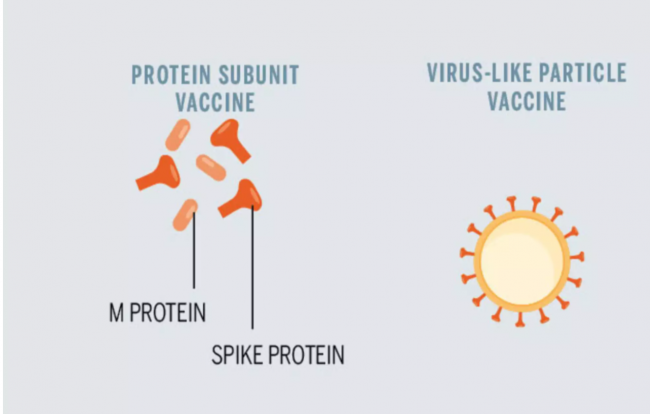
- The protein subunit vaccine, which consists of harmless fragments (proteins) of the virus that cause the COVID-19, instead of the entire pathogen. After being vaccinated, our bodies recognize that the protein should not be there and make T lymphocytes and antibodies, which will remember how to fight the COVID-19 virus if we become infected. Future.
- Vaccine Vector or recombinant vector vaccine, Vaccine AstraZennca, Johnson & johnson, Sputnik V are vaccine vectors. How the vector vaccine works is that it contains a modified version of a virus that is different from the COVID-19 pathogen, eg Adenovirus. The inside of the modified virus cell contains material from the COVID-19 pathogen virus. This material is known as a "virus vector". After the viral vector enters our cells, the genetic material provides the cell's instructions to make its own proteins with the COVID-19 virus. Using these instructions, our cells make copies of those proteins. This prompts our bodies to make T and B lymphocytes remember how to fight the virus if we become infected in the future.
Mechanism of action of the vector vaccine:
Some COVID-19 vaccines require more than one dose
To get the full immunizations, you will need two doses for some COVID-19 vaccines.
If you get the COVID-19 vaccine that requires two doses, you are considered to have been fully immunized only two weeks after the second dose. The COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer- BioNtech and Moderna, AstraZennca requires two doses.
If you get the COVID-19 vaccine that requires one dose, you are considered to be fully vaccinated two weeks after the shot is given. The COVID-19 vaccine from Johnson & Johnson's Janssen requires a single injection.
If you have had the injection for less than two weeks or still need a second dose, then you are NOT fully protected. Continue to take all preventive steps until complete vaccination (two weeks from the last dose).
Conclude
Getting a vaccine is one of the many things we can do to protect ourselves and others from COVID-19. Protection from COVID-19 is especially important for some people, as COVID-19 can cause serious illness or death.
Preventing a pandemic requires using all the tools available. The vaccine works with our immune system to make your body ready to fight covid -19 if you are exposed. After we have been fully vaccinated against the Covid-19 room, we can begin to do some of the things that we have had to stop due to the pandemic. However, we are still looking at the effect of a vaccine on the spread of COVID-19. Once fully vaccinated against COVID-19, we should also continue to take precautions (5K) in public or when you are around unvaccinated people from more than one household. family.
Getting COVID-19 vaccination and following the CDC recommendation to protect yourself and others provides the best protection against COVID-19.
The article has references from WHO and CDC US documents.
Other news
- May 19 morning: Vietnam has 31 new COVID-19 cases, the Ministry of Health consults with a 'record' of 20 severe cases ( 08:51 - 19/05/2021 )
- May 06, an additional 8 cases COVID-19 at the Tropical Disease Hospital Central ( 10:10 - 06/05/2021 )
- This morning 5-5, Vietnam has no new cases of COVID-19, more than 602,000 more globally ( 14:29 - 05/05/2021 )
- On the morning of May 3, Vietnam did not record a new case of Covid-19 infection ( 07:56 - 03/05/2021 )
- On the morning of March 1, no cases of COVID-19, 210 patients undergoing treatment were negative ( 08:28 - 01/03/2021 )
- On the morning of February 25, there was no new case, a patient with very severe COVID-19 ( 08:35 - 25/02/2021 )
- How to wear a Mask properly ( 09:01 - 22/02/2021 )
- 39 provinces and cities let students stop going to school ( 09:47 - 17/02/2021 )
- COVID-19 'brutally exposes' the technological gap ( 15:29 - 30/01/2021 )
- Hanoi added cases of COVID-19, this morning 9 new cases in the community of 5 provinces ( 09:39 - 29/01/2021 )