Contact Admission
International Collaboration
Microscopic robot in laparoscopic surgery
Microscopic robot in laparoscopic surgery
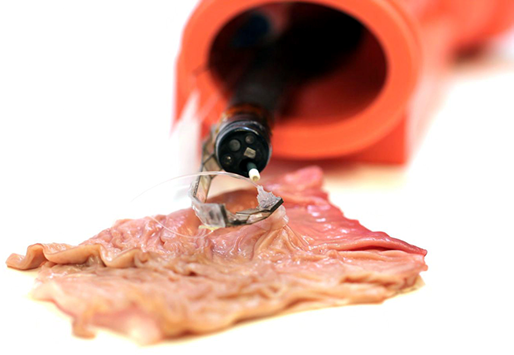
Researchers at Harvard University have developed a new endoscopy device called the "Soft Robotic Arm" soft robotic arm. The device is placed flat inside the endoscope because it has to pass through narrow areas of the human body, but can dissect many parts of the body when needed.
An endoscope is a flexible tube probe that allows the surgeon to pass through narrow areas of the body to perform surgery. Usually, this probe has rigid surgical instruments attached to the head. This rigid device can make it difficult for the endoscopist to operate it correctly and safely, as it can inadvertently damage the soft tissues of the patient's body.
This problem motivated scientists at Harvard University to develop a soft robotic arm to perform their laparoscopic manipulation. However, the development of this robotic device has also brought a number of challenges for scientists. "On scale millimeters, a robotic device can become soft enough, not to cause damage to the tissues inside the body, but it cannot perform the necessary maneuvers. "Microscopic Technologies in Surgery. The question is: How can we develop soft robotic devices that can both perform the necessary surgery and make patients safe".
"We discovered that, by integrating liquid microprocessors into hard device architectures," said Sheila Russo, a graduate student in Applied Science & Engineering at Harvard University. can create a sophisticated, soft-working mechanical part that increases the actuator's performance in terms of force, in addition to its ability to predict and control motion. lie flat inside the endoscope while it is directed to the location the surgeon wants, where doctors can deploy a soft system that can safely and effectively interact with tissues in the body. ".
This device can effectively interact and manipulate soft tissues and is useful for a wide variety of surgical procedures. It uses a suction nozzle to achieve this effect, which is inspired by the suction senses on the octopus tentacles. The device can also be scaled up to 1mm, allowing surgeons to use it in other endoscopic procedures, such as those in the brain or lungs.
Source: www.medgadget.com
Translator: Dr .Nguyen Huu Tung & partner
Other healthcare
- Development history of world medicine ( 11:44 - 13/10/2017 )
- Microfluidic channel device for tumor chemotherapy ( 11:40 - 12/10/2017 )
- Higher education in the era of Industrial Revolution 4.0 ( 11:37 - 08/11/2017 )
- DRG Nerve Stimulant Device ( 11:19 - 09/10/2017 )
- Surgeons view CT, MRI, ultrasound images using 3D technology ( 11:14 - 07/10/2017 )
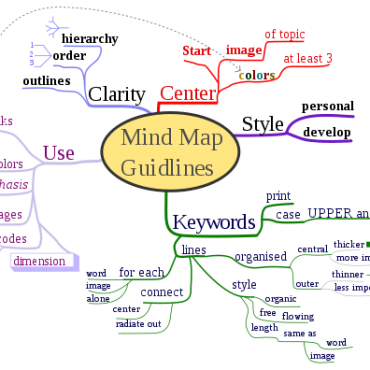
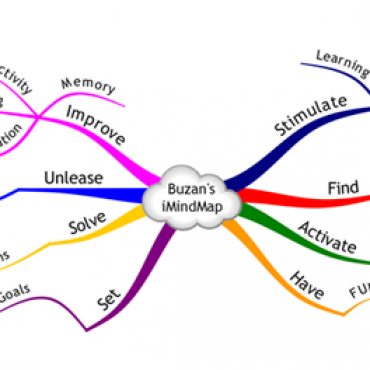
- Steps to make mind map (Mind map) ( 11:00 - 07/10/2017 )
- Mind mapping software ( 10:41 - 07/10/2017 )
- Mind map is what? ( 10:28 - 18/10/2017 )
- Schizophrenia is 80% hereditary ( 10:21 - 05/10/2017 )
- Ten ancient pain relievers ( 15:20 - 06/10/2017 )